Phyton python floor division operator python floor division example python floor the expression 6 4 yields 1 where floor division produces the whole number after dividing a number.
Python floor division negative numbers.
For positive numbers there s no surprise.
Floor division with operator note.
5 2 2 but if one of the operands is negative the result is floored i e rounded away from zero towards negative infinity.
7 2 3 but python is giving output 4.
Python 2 s operator performs floor division where for the quotient x the number returned is the largest integer less than or equal to x.
The rounding towards zero behavior was deprecated in python 2 2 but remains in python 2 7 for the sake of backward compatibility and was removed in python 3.
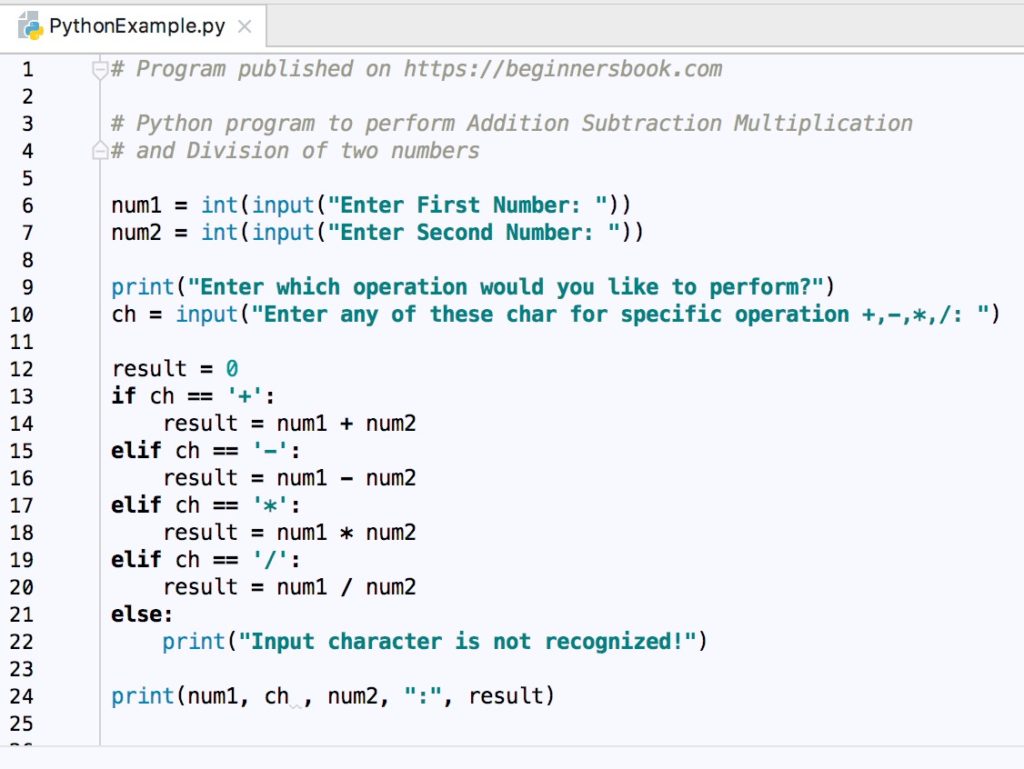
Division works differently in python 2 and 3.
The above example of 2 3 which gives 0 in python 2 shall be used as 2 3 0 or 2 0 3 or 2 0 3 0 to get 0.
Python s default division of integers is return the floor towards negative infinity with no ability to change that.
Mathematically python is not giving correct output for integer division for negative number e g.
In python 2 the quotient returned for the expression 11 2 is 5.
You can read the bdfl s reason why.
I hope you learnt something new and if you re looking to upgrade your python skills even further you might want to check out our complete python course.
Python 3 s approach provides a fractional answer so that when you use to divide 11 by 2 the quotient of 5 5 will be returned.
Tim peters who knows where all python s floating point skeletons are buried has expressed some worry about my desire to extend these rules to floating point modulo.
But for floor division in python 2 int int int to understand m.
The truncate towards negative infinity rule can cause precision loss for x 1 0 when x is a very small negative number.
To do round up division you would use.
I was asked again today to explain why integer division in python returns the floor of the result instead of truncating towards zero like c.
To get a float result in python 2 without floor rounding we can specify one of the operands with the decimal point.
5 2 3 5 2 3.
Floor division and modulo are linked by the following identity x x y y x y which is why modulo also yields unexpected results for negative numbers not just floor division.
Ordinary division with operator 2.